Real estate balance sheet / profitability: income properties, real estate purchase and cash flow optimisation
Real estate balance (Source: Alex Fischer) – Do you want others to help build your wealth? In this video, you’ll learn how certain income properties can give you another six for every one you pay! A comprehensive look at the economic part of real estate, both for cash investors, those who buy real estate for investment reasons, and owner-occupants. To start with, a short and simple summary: Imagine getting something for 10,000 euros that has a value of 100,000 euros. So not 100.000 Euro in 30 years, you get a value of 100.000 Euro immediately. Example: you buy a Porsche that has a value of 100.000 Euro, but you only have to pay 10.000 Euro for it and you already get this Porsche delivered. You don’t have to pay the 10.000 Euro immediately, but little by little. How would you like that? Get to know the principle of real estate.
Real estate balance sheet: investment to surplus
If you don’t have the possibility to watch the video (plane, train, etc.): You can find the transcript with all tips directly below the video.
Tip. Taxes, finances: It’s a boss thing. I’ve been following Alex as a real estate investor for almost a year. Most recently I also attended his tax coaching, read more about that time and what I learned in tax coaching here: Alex Fischer Experience.
How real estate works as an investment
you actually only have to pay 10,000 euros once and immediately get a value of 100,000 euros. Once again, you don’t have this value of 100,000 euros in 30 years, but you have it immediately, the increase in value can take place immediately. How does that work? I’m going to show you right now!
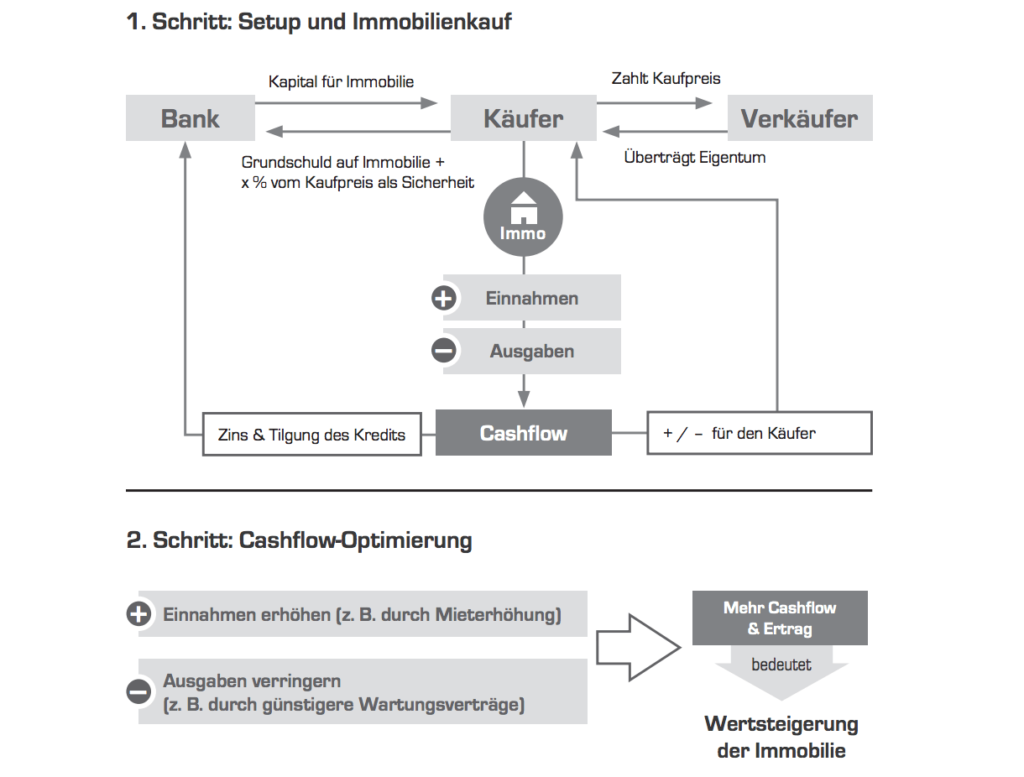
The interesting thing about real estate is, real estate is a balance sheet. That means it has an income side and an expense side. Another special feature of real estate is that you don’t have to have 100,000 euros. Normally, if you want to invest money in a share fund or in a building society, you have to have 100,000 euros in order to make a 100,000 euro building society or 100,000 euro investment.
Here’s how it works with real estate: If you earn well enough, for example. I.e. you have a net income of more than 2,000 euros as a single person or more than 2,500 euros as a married person. Then this means that you already pay taxes, that you have a good name for the bank. This means that the bank thinks you are a good customer. For this reason, the bank lends you 100,000 euros and takes the property as collateral.
Reading Tip! Real estate financing: How does the bank think?
Now let’s look at that record.
Income and expenditure side of a property
I have already said: The balance sheet has an income side and an expenditure side. On the income side, the first factor is “rent”. Here we calculate approximately with a size of 5% rental income, which corresponds to 5,000 euros per year. Then we have a tax advantage. This corresponds approximately to 1% per year, which would be 1,000 euros. That would be the income side. The expenditure side: there we have interest; important with the interest, this is debt interest. you have borrowed money and you have to pay debt interest to the bank, for the fact that you have debts with the bank. That’s sort of the loan fee on the money. Not to be confused with interest on credit. That’s different. That’s when the bank owes you money, then you get money. We’ll put this interest at 4%. That would be about 4,000 euros.
In fact, interest rates are even lower at the moment. But I prefer to calculate a little longer term and a little worse for the property, so that you see that even in the case of an interest rate increase, the whole thing would still work. On the subject of interest rate increases, etc. you will learn a lot later.
Revenue side of the balance sheet:
- Rental income (5%) = 5,000 Euro / year
- Tax advantage (1%) = 1,000 Euro / year
expense side of the balance
- Debt interest (4%) = 4,000 Euro / year
What is important in this example is to understand the principle of real estate.
Redemption and disruptive factors
Now let’s move on to repayment. Repayment is nothing more than the repayment of the money. Interest is the loan of money, repayment is the repayment. So you make sure that the debt becomes less and less.
We now set the repayment here in the example at 2%. That corresponds to a term of about 25-30 years. This corresponds to 2,000 euros per year. Then we have costs that we have to calculate. These include maintenance, for example, if something needs to be repaired on the property, or the costs for property management. These cannot be transferred to the tenant. In other words, these are costs that you really have to pay out of your own pocket. These can be calculated with 1%, a good average value, which corresponds to 1,000 euros in this example.
Calculate own investment: After repayment and costs
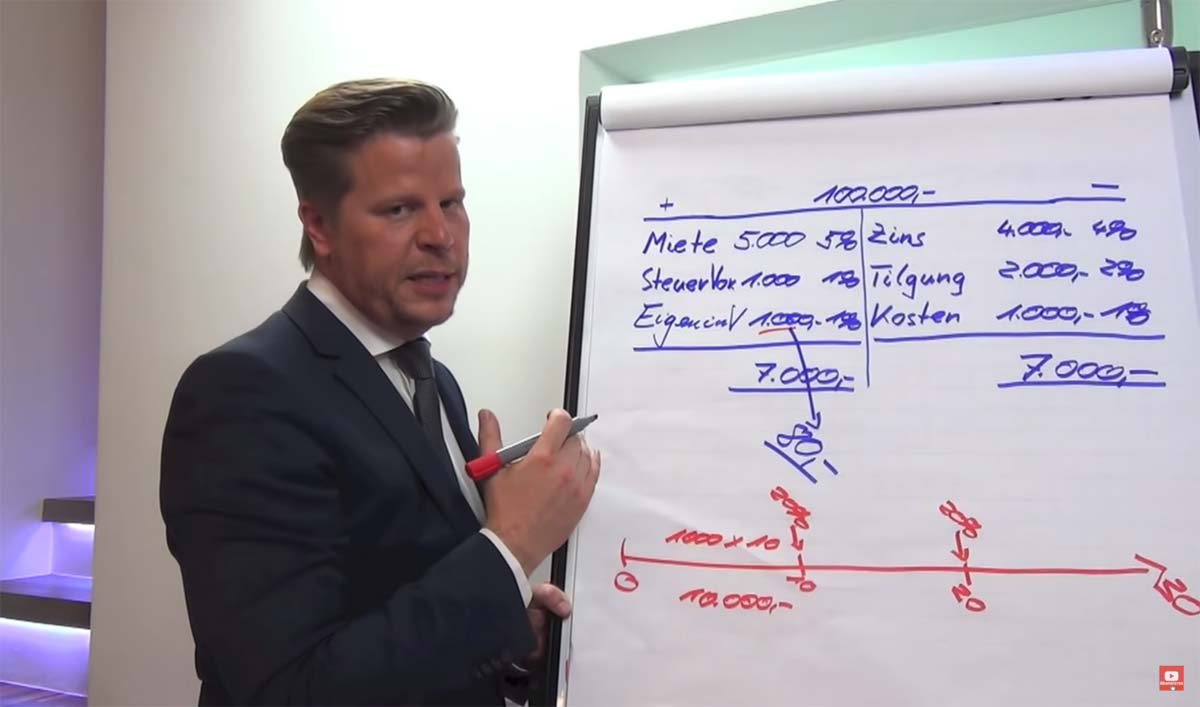
Now we draw a line. 4,000 euros plus 2,000 euros plus 1,000 euros, that’s a total of 7,000 euros a year. A balance sheet must be balanced.
New on the expense side:
- Repayment (2%) = 2,000 Euro / year
- Duration: 25-30 years
- Running costs (1%) = 1,000 Euro / year
- [Debt interest (4%) = 4,000 euros / year from above].
If we add it up now, we see “Gee, there’s 1,000 euros missing”. That is the personal investment. We set this calculated to 1%, so 1,000 euros, mind you, per year. Means with a 100,000 euro real estate that are approximately 80 euro in the month. For these 80 euros a month we get a property worth 100,000 euros. Now I told you before that the great thing about real estate is that you have to invest 10,000 euros once and not even immediately, but in installments. For that you get immediately a value of 100,000 euros.
This (screenshot) is a time track. Starting in the year zero. That would be the year of purchase. In year 30, that’s the year the property is paid off. The property with 2% amortization would be paid off in about 30 years. Why and why, I’ll explain later. Now, I’ve simply marked intermediate years here: Year 10, Year 20. So we have to pay (initially) 1,000 euros of our own contribution per year. That means we pay 1,000 euros a year, times 10 years. So in total we have to pay 10,000 euros.
Excerpt (video above, 6:15 minutes)
Source: Alex Fischer Youtube
Factor rent increase and term
Then let’s say this: In year 10, we increase the rent by 20% on a one-time basis. Of course, no one does that, but the point here is to understand the principle of real estate and that’s why we keep it simple. We do not increase every year in a row, in a small percentage, but we do nothing for 10 years and then increase once by 20%.
Calculation example: Zero runner
Then after 20 years we do the same game again. Now let’s look at how that affects our balance sheet. In year 10 we increase by 20%, that is 5,000 euros is our previous rent, we increase that by 20%, then all of a sudden we have 6,000 euros rent. 6,000 euros rent plus 1,000 euros tax advantage, is 7,000 euros, 7,000 euros we need, that is, our own investment falls away. So that means from year 10 to 20 we’re paying plus minus zero all the time.
- Rent (first 9 years): 5.000 Euro / year
- Rent (10-19 years): 6.000 Euro / year (+20%)
- Plus tax advantage (above): 1,000 euros / year
- Total income: 7.000 Euro / year
- Own investment (from year 11): 0 Euro
Calculation example: Positive cash flow
Then in year 20 we increase the rent again by 20%. That would be here, 20%, we now have 6,000 euros rental income, means we then have 7,200 euros rental income. Means we now have plus 1,200 euros here. Why? 7,200 euros we have, 1,000 euros tax advantage is 8,200 euros, 7,000 we need only, that is, we have a surplus of 1,200 euros. Means: In year 20-30 we get plus 12,000 euros back out.
- Rent (20-29 years): 7,200 euros / year (+20%)
- Plus tax advantage (above): 1,000 euros / year
- Total income: 8.2000 Euro / year
- Surplus: 1.200 Euro / year
Optimize cash flow and automate process
You need to sharpen your eye for “cash flow opportunities” (ways to generate passive cash flow) first. Learn more about optimizing cash flow and automating your process here. How to increase your cash flow (external).
- Step: Real estate financing and purchase
- Step: Optimize cash flow
Source: Alex Fischer
Real value of a property: value stability against inflation
But now I originally said we have to invest 10,000 euros once to get a property for 100,000 euros immediately. That’s because I didn’t take that part into account here. Because I leave this part for the unforeseen. For example, the apartment might not be rented out at some point or it might need a major repair. Another advantage of real estate is that normally if you have 100,000 euros of credit, inflation reduces that credit every year.
3% inflation leaves you with only 97,000 euros after one year, or 40,100 euros after 25 years.
The beauty of real estate is you have a tangible asset, that tangible asset increases in value due to inflation. How this works exactly, we explain again in further lessons.
Loan decreases, asset value increases
Credits are positive monetary values, loans are negative monetary values. The loan with which you bought the property is a kind of negative monetary value. This negative monetary value, of course, is also subject to inflation. That is:
After 30 years, 100.000 Euro debts, i.e. negative monetary value, are only worth 40.100 Euro.
This scissor that property goes up and debt goes down at the same time is what’s really fun with real estate.
Remember: Creditworthiness is everything
One or two of you may be asking yourselves, gosh, if this is so awesome. Why doesn’t everyone do it? Quite simply, not everyone can do it. In order to do it, you have to a) pay proper taxes and b) have a good name with the bank. When does one have a good name at the bank? When you earn at least 2,000 euros net as a single person or at least 2,500 euros net as a married person.
Real estate or investment fund?
Real estate or investment fund? The difference between real estate and a conventional investment is that you could never have a full 200,000 euros with 5,000 euros in a conventional investment. That will never work. With investment property it does. Why it is smart to invest your money in real estate instead of, for example, in funds and how real estate works as an investment, I’ll explain here!
- Real estate or investment fund? (external)